SUPPLEMENTARY: 2
Helicine arteries (LP)
|
This is a low power picture showing a large part of the penile urethra (1) lined by a stratified columnar epithelium. Mucous secreting paraurethral glands (2) open into the deep outpocketings of urethra. The secretions of these and the bulbo-urethral glands (Cowper's glands) lubricate the urethra.
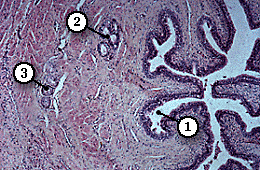
Helicine arteries (3), which normally supply the erectile tissue, can also be seen in this section and at higher power in the section below. Because they have a spiral course they are seen in several planes of section. They are anastomosing arteries and arterioles with thick, muscular walls which are supplied by the parasympathetic nervous system. Blood drains from the tissues into the large veins which lie immediately deep to the dense connective tissue of the tunica albuginea.
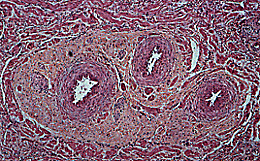
Sexual excitement causes parasympathetic mediated relaxation of the smooth muscle in the walls of the helicine arteries and the cavernous sinuses, allowing an increase in blood flow to the penis. The cavernous spaces become engorged with blood, venous return is restricted as the veins become compressed against the tunica albuginea and the cavernous spaces become turgid with blood causing erection of the penis.
Tutorial Navigator:


