 SUPPLEMENTARY:
SUPPLEMENTARY: SUPPLEMENTARY:
SUPPLEMENTARY:
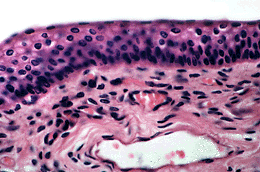
Metaplasia (HP) | Core | Supplementary Material on Respiratory Epithelium | ||
| Return to Core | specialisations of respiratory epithelium | goblet cells & cilia | cilia |
| EM of cilia (TS) | pathological increase in goblet cells | metaplasia of the respiratory epithelium | Return to Respiratory System Main Index |